The Hyoid Bone - Your Body's Unique Floater
Have you ever stopped to think about the incredible workings of your own body? There are so many small parts that do really big jobs, and one of them, a rather interesting one, is the hyoid bone. This tiny, horseshoe-shaped bone is quite special, you see, as it's the only one in your entire body that doesn't actually touch or connect with any other bone. It just sort of floats there, a bit like a tiny island, and yet it plays a truly significant part in how you talk, how you breathe, and even how you eat. It’s a pretty neat piece of anatomical design, wouldn't you agree?
This little bone, which is sort of shaped like the letter 'U', makes its home right in the front part of your neck. It sits comfortably between your chin and that part of your throat often called the Adam's apple, which is your thyroid cartilage. It's almost as if it's holding court in that spot, providing a vital anchor for your tongue and the area around your throat. Without it, many everyday actions we take for granted would be, you know, quite a bit more difficult.
So, if you're curious about this amazing, freestanding bone, you've come to the right spot. We're going to take a closer look at where it lives, what it does, and how it’s put together. We'll also explore what happens when it runs into a bit of trouble and how folks go about fixing things. It’s a pretty fascinating bit of anatomy, actually, and learning about it might just give you a new appreciation for the quiet work happening inside you.
Table of Contents
- What is the Hyoid Bone, Anyway?
- The Hyoid Bone - A Unique Design
- Where is the Hyoid Bone Found?
- How Does the Hyoid Bone Work?
- The Hyoid Bone's Important Connections
- What are the Parts of the Hyoid Bone?
- Can the Hyoid Bone Have Troubles?
- Looking After Your Hyoid Bone's Well-being
What is the Hyoid Bone, Anyway?
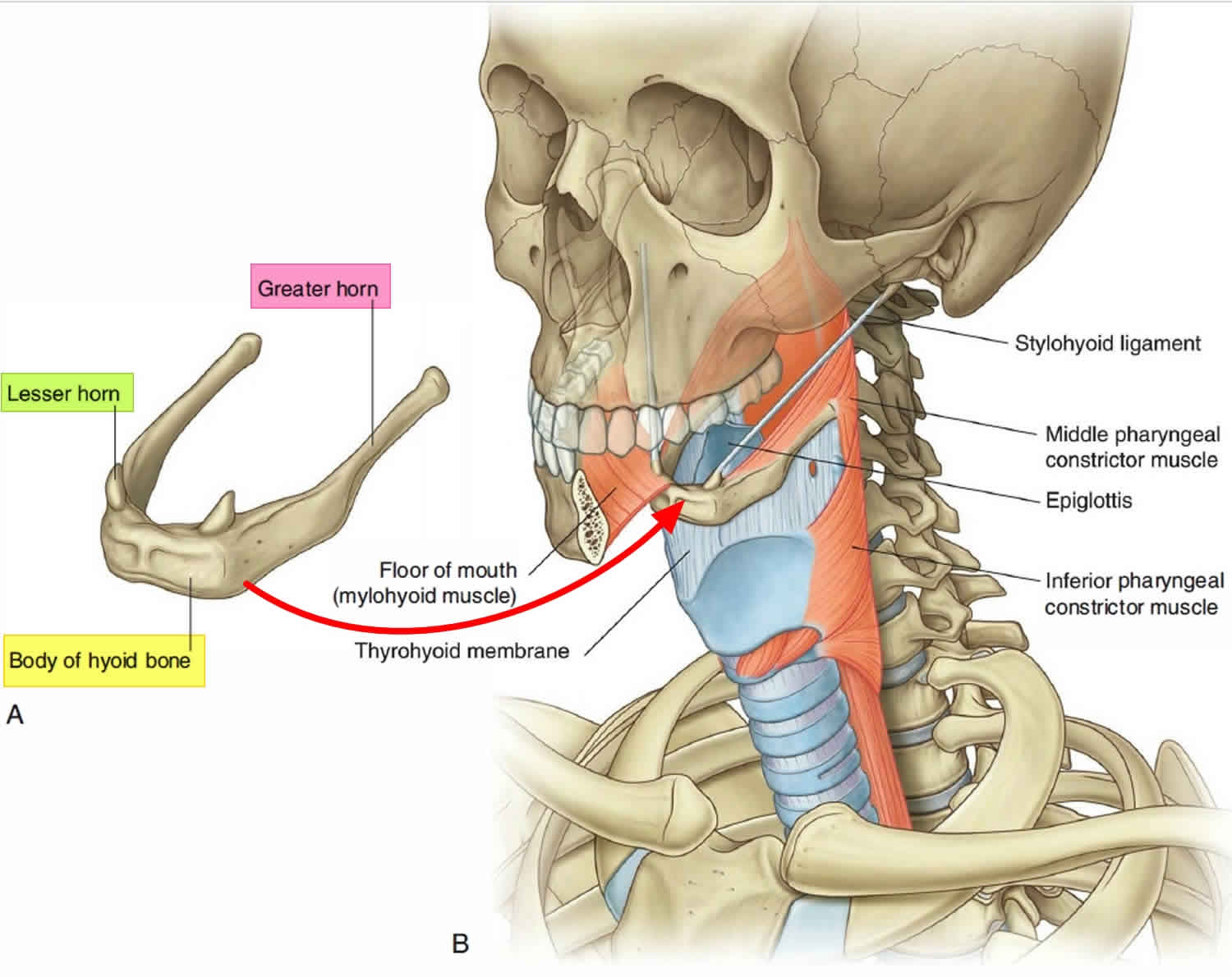
The hyoid bone is, quite simply, one of a kind in your body. It's often called the "floating bone" because, unlike nearly every other bone you possess, it doesn't form a joint with any other bony structure. This is a pretty unusual feature, you know, making it stand out from the crowd. It’s a bit like a small, isolated piece of architecture that supports a whole system of movement and action. Its name, in fact, comes from a Greek word, 'hyoeides', which means "U-shaped," a good description of its form, you know, if you were to see it up close.
This bone is also sometimes put into a group of bones called sesamoid bones. That classification means it's a bone that is, in a way, embedded within a tendon or muscle, allowing it to move freely. This freedom of movement is what gives it its special ability to help with things like speaking and swallowing. It’s almost as if it’s a tiny, independent operator, yet it works in perfect harmony with the rest of your body’s complex systems. So, it's not just a floating bone, it's a very active floating bone, you might say, playing a rather important role.
The hyoid bone, despite its small size, is a truly central player in the mechanics of your head and neck. It acts as a kind of movable base for your tongue, and it also provides a stable spot for various muscles and tissues that help you get food down your throat and make sounds. Without this little bone, your tongue would have a much harder time doing its job, and speech would be, well, quite different. It's pretty amazing how one small, unattached bone can be so deeply involved in such important daily activities, isn't it?
The Hyoid Bone - A Unique Design
When you look at the hyoid bone, you'll see that 'U' shape we talked about, which is a pretty clear visual marker. This shape isn't just for show, you know, it's quite functional. It allows for a broad surface area where various muscles and connective tissues can attach. These attachments are what give the hyoid bone its ability to move and support other structures, especially during actions like swallowing and speaking. It's a design that, in a way, seems simple but is actually quite effective for its purpose.
The bone itself is made up of five main parts, or segments, if you want to be more precise. These segments come together to form the overall 'U' shape, and each part plays a role in how the bone functions. The way these segments develop, a process called ossification, is also pretty interesting, as it contributes to the bone's unique structure and how it sits within the neck. It's a gradual process, but it results in a strong yet flexible little bone that can handle a lot of movement, you see.
Because of its particular design, the hyoid bone can act as a kind of pulley system for the muscles that connect to it. This mechanical advantage helps to control the position of the tongue and the opening of the throat. It's almost like a tiny lever that helps to make big movements possible. This structural setup, with its various parts working together, is really what makes the hyoid bone so good at its job, enabling smooth and coordinated actions in your mouth and throat, you know, all the time.
Where is the Hyoid Bone Found?
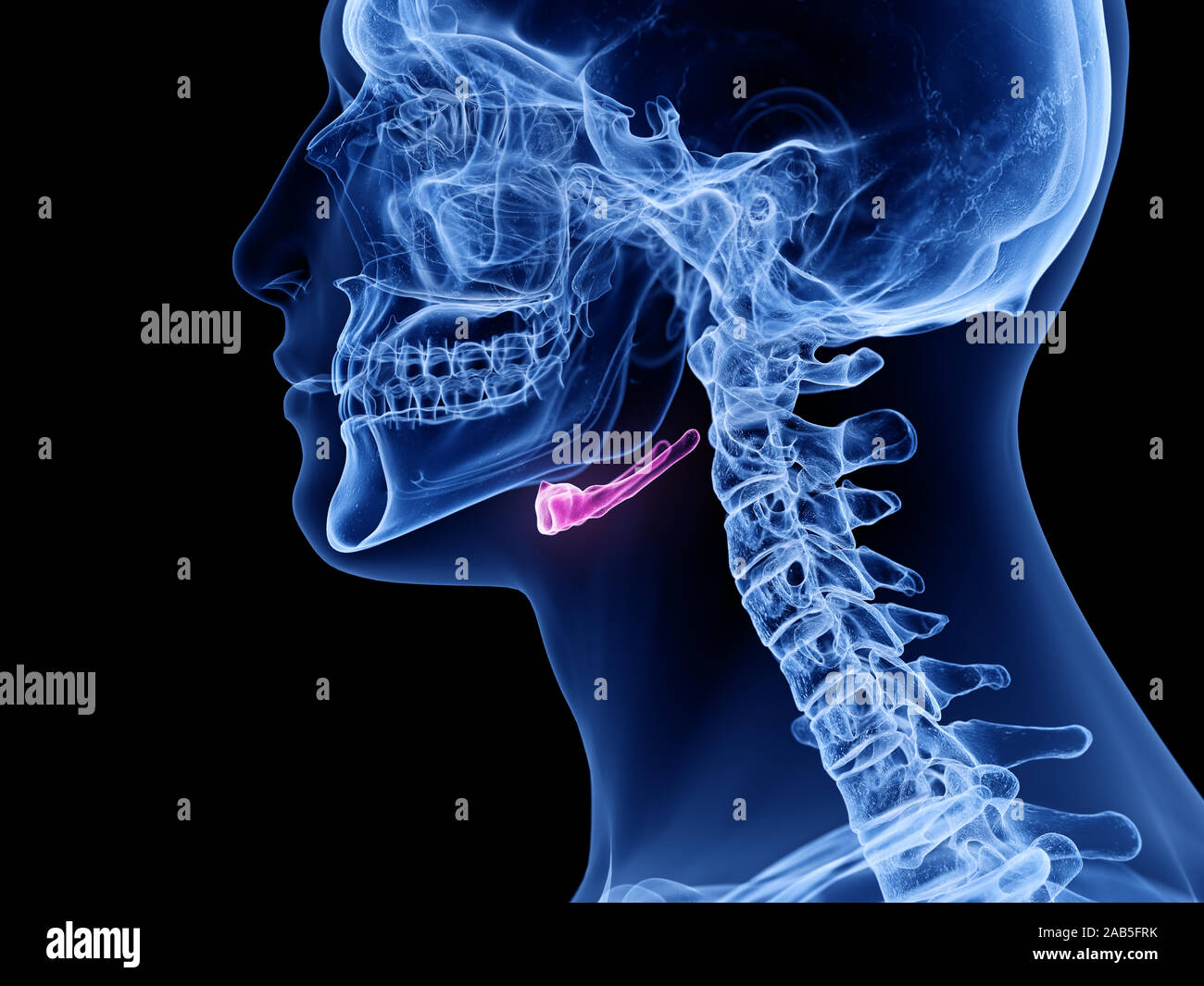
So, where exactly does this unique hyoid bone make its home? If you were to point to it, you'd find it right in the front of your neck, sitting between your chin and the part of your throat that some people call the Adam's apple. That's the thyroid cartilage, to be more exact. It’s placed in a spot that makes it just right for supporting the structures of your tongue and throat, you see, a very strategic location, if you think about it.
When you're just resting, perhaps sitting quietly, the hyoid bone typically lies at a certain level. It's usually around the same height as your lower jaw, or mandible, in the front of your face. And if you were to look at your neck from the side, it would generally be at the level of the third bone in your neck's spine, which is called the third cervical vertebra. This consistent positioning, you know, helps it to maintain its supporting role for the muscles and tissues connected to it.
To put it another way, the hyoid bone is positioned just below your lower jaw and just above that protective tissue that covers your voice box. It’s a bit like a bridge connecting these two areas, providing a stable point for everything to work from. This placement is pretty important, as it allows the hyoid bone to play its part in so many different functions, from the simple act of breathing to the more complex actions of speaking and swallowing, you know, every single day.
How Does the Hyoid Bone Work?
The main job of the hyoid bone is to serve as an attachment point. Think of it like a central anchor for a whole bunch of muscles and connective tissues that are involved in moving your tongue and the structures around your throat. It’s not just a passive spot, though; it plays a truly active part in holding things in place, allowing these muscles to pull and push against a stable base. This anchoring role is, you know, pretty essential for a lot of what goes on in your mouth and neck.
This little bone is very much involved in the process of swallowing. When you swallow, a complex series of muscle actions takes place, and the hyoid bone moves up and forward, helping to open the passageway for food and drink to go down. It’s almost like a little elevator that helps to guide things along. Without its proper movement, swallowing could become quite difficult, so it's a pretty big player in that everyday function, you might say.
Beyond swallowing, the hyoid bone also has a very important part in speech and breathing. The muscles that control your tongue and the position of your voice box are connected to it, and their movements allow you to form different sounds when you talk. And when you breathe, the hyoid bone helps to keep your airway open, preventing it from collapsing. So, despite its size, it really does have a pivotal role in these basic, life-sustaining activities, you know, keeping everything running smoothly.
The Hyoid Bone's Important Connections
The hyoid bone might float free from other bones, but it is certainly not alone in your body. It has a remarkable number of muscles and ligaments that attach to it, creating a complex web of connections. These attachments are what give the hyoid bone its ability to move and, in turn, move other structures. It's almost like a central hub where many different pathways meet, all working together for a common purpose, you know, like a very busy crossroads.
There are muscles that come from above the hyoid bone, connecting it to your lower jaw and the base of your skull. These muscles help to pull the hyoid bone upwards and forwards. Then, there are muscles that come from below, connecting it to your breastbone and shoulder blade, which help to pull it downwards. This push-and-pull system, you see, allows for a wide range of motion, which is necessary for all the actions it supports.
In addition to muscles, various ligaments and membranes also attach to the hyoid bone. These connective tissues help to hold the hyoid bone in its proper place and provide extra stability, while still allowing for flexibility. They ensure that the hyoid bone can move smoothly during swallowing and speaking without getting out of position. So, it's not just about the muscles; these other connections are pretty vital too, ensuring everything stays where it should be and works as it ought to, you know, quite efficiently.
What are the Parts of the Hyoid Bone?
The hyoid bone, despite its somewhat small overall size, is not just one solid piece. It’s actually made up of several distinct parts that come together to form its characteristic 'U' shape. These parts include a central body and two pairs of projections, often called horns or cornua, which extend outwards. It’s a bit like a miniature anchor with its various arms, you know, giving it a very specific structure.
The development of the hyoid bone, how it forms and hardens over time, is a process known as ossification. This process involves the transformation of cartilage into bone, and it happens in different stages for each of its parts. The way these parts develop and fuse together contributes to the bone’s strength and its ability to withstand the forces exerted by the many muscles attached to it. It’s a pretty neat bit of biological engineering, actually, that allows it to be so effective.
Each of these parts of the hyoid bone provides specific points for muscles and ligaments to attach. The body, for instance, offers a broad surface for many connections, while the horns provide more defined points for certain muscle groups. This segmented structure allows for a very precise and coordinated movement, which is essential for the complex actions of the tongue and throat. So, it’s not just a simple bone; it’s a rather intricately put-together structure, you know, for all its important tasks.
Can the Hyoid Bone Have Troubles?
Even though the hyoid bone is quite strong and well-protected, it can, like any other part of the body, sometimes run into problems. One such issue could be a fracture, which means the bone has broken. While not super common, a fracture of the hyoid bone can happen, for example, due to a direct impact or certain types of physical stress. When it does, it can be pretty painful and make it difficult to swallow or speak, you know, causing a lot of discomfort.
Beyond fractures, the hyoid bone can also, though rarely, become dislocated. This would mean it has moved out of its normal position, which can disrupt its ability to function properly. There are also some very rare conditions or syndromes that can affect the hyoid bone, impacting its shape or its ability to move as it should. These sorts of issues can sometimes lead to difficulties with breathing or swallowing, so they are, you know, quite serious matters.
Interestingly, the hyoid bone can also be affected by conditions like sleep apnea. In some cases, the way the hyoid bone and its connected muscles are positioned during sleep can contribute to the airway becoming blocked. Understanding how the hyoid bone plays a part in such conditions is, you know, pretty important for diagnosing and treating them. If someone is having issues with their hyoid bone, medical professionals will look at its structure, its connections, and its movement to figure out what’s going on and how best to help.
Looking After Your Hyoid Bone's Well-being
Since the hyoid bone is so important for everyday actions like speaking, swallowing, and even breathing, keeping it healthy is, you know, pretty much a good idea. While you can't exactly "exercise" your hyoid bone directly, looking after your general neck and throat health can certainly help. This includes things like maintaining good posture, which can affect the alignment of your neck structures, and being mindful of any unusual pain or difficulty in the throat area.
If someone experiences symptoms that suggest a problem with their hyoid bone, such as persistent pain in the front of the neck, difficulty swallowing, or changes in their voice, it’s a good idea to seek advice from a healthcare professional. They can use various methods to figure out what’s going on, like physical examinations or imaging techniques, to get a clear picture of the hyoid bone’s condition. It’s pretty important to get a proper diagnosis, you know, to ensure the right steps are taken.
Once a problem with the hyoid bone is identified, there are typically ways to help. Treatment might involve things like rest, pain management, or, in some cases, specific therapies to help restore its function. For instance, if sleep apnea is related to the hyoid bone’s position, there might be particular approaches to address that. The goal is always to restore comfort and function, ensuring this unique bone can continue to do its very important jobs smoothly, you know, for the long term.

hyoid bone | Description, Anatomy, & Function | Britannica
Hyoid bone anatomy, location, dislocation, fracture & hyoid bone syndrome
Hyoid bone hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy